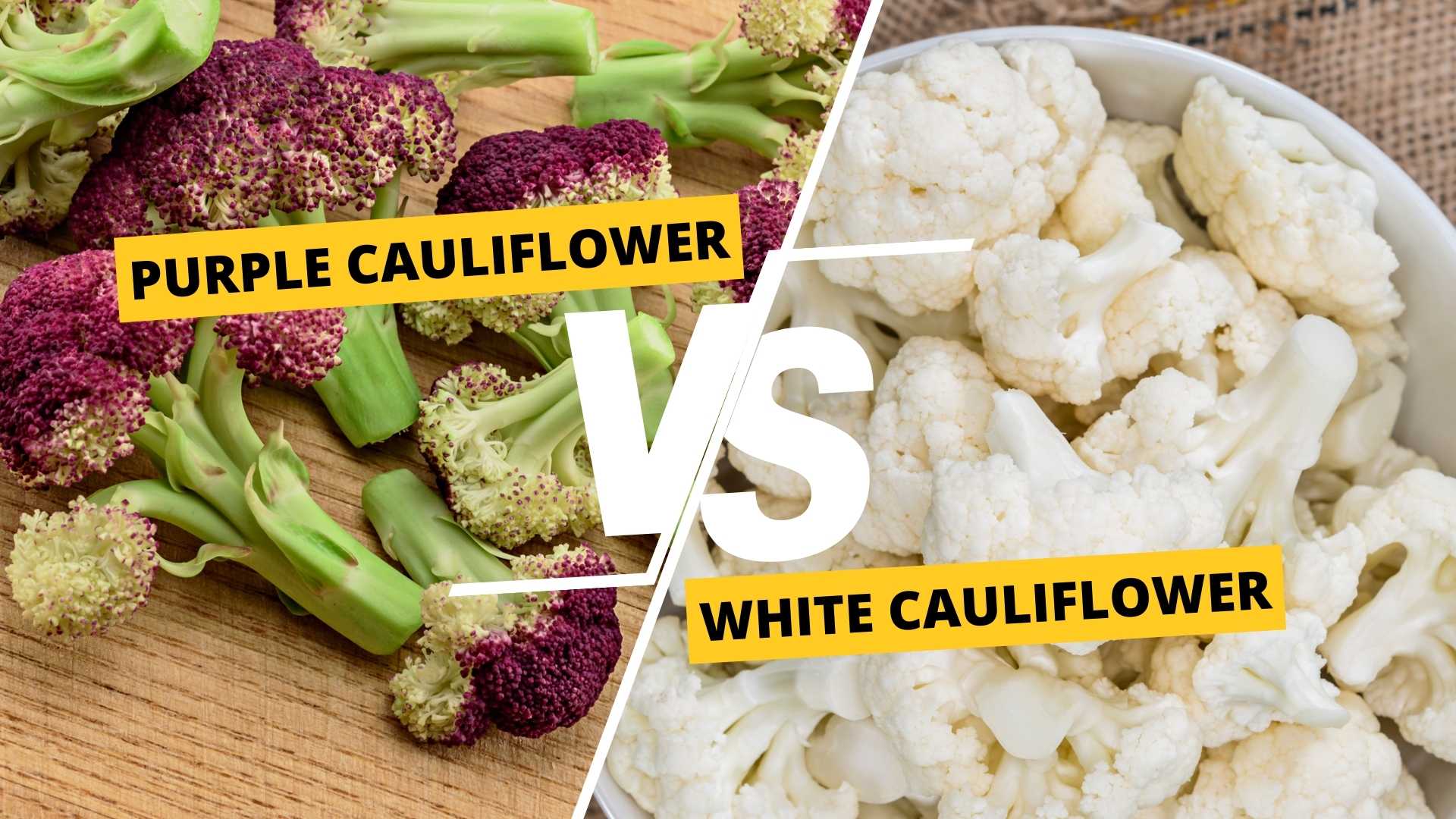
Cauliflower is a popular and versatile vegetable that belongs to the Brassica family. It is packed with various vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, making it an excellent addition to any diet.
There are different types of cauliflower, including white, purple, green, and orange, each with a distinct flavor and nutritional profile. In this article, we will focus on the nutritional differences between purple and white cauliflower and its potential health benefits.
The Similarities between Purple and White Cauliflower
Purple and white cauliflower share many similarities, such as their nutrient content, potential health benefits, culinary versatility, and cost and availability.
Nutrient Content
Both purple and white cauliflower is rich in essential vitamins and minerals. They are a good source of vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin B6, folate, and potassium. They are also low in calories and carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for people who are watching their weight or managing their blood sugar levels.
Potential Health Benefits
Purple and white cauliflower offer numerous potential health benefits. They are high in antioxidants that help protect against oxidative stress and chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. They also have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation in the body and alleviate symptoms of arthritis, asthma, and other inflammatory conditions.
Culinary Versatility
Both purple and white cauliflower are versatile in the kitchen. They can be roasted, grilled, steamed, sautéed, mashed, pureed, and added to soups, salads, and stir-fries. They can also be used as a low-carb substitute for rice, potatoes, and pasta.
Cost and Availability
Purple and white cauliflower is widely available in most supermarkets and grocery stores. They are relatively affordable and can be found fresh, frozen, or canned.
The Differences between Purple and White Cauliflower
Purple and white cauliflower differ in several ways, including their anthocyanin content, flavor profile, cooking techniques, and visual appeal.
Anthocyanin Content
The most significant difference between purple and white cauliflower is their anthocyanin content. Anthocyanins are natural pigments that give fruits and vegetables their distinctive purple, blue, and red colors. Purple cauliflower contains higher levels of anthocyanins than white cauliflower, making it a more potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory food.
Flavor Profile
Purple cauliflower has a slightly sweeter and nuttier flavor than white cauliflower. Its flavor is milder and less earthy than that of its white counterpart. However, when cooked, the two varieties have a similar taste.
Cooking Techniques
Purple and white cauliflower can be cooked using different techniques. White cauliflower is more delicate and cooks faster than purple cauliflower. It is best steamed, roasted, or sautéed to preserve its texture and flavor. Purple cauliflower is denser and takes longer to cook than white cauliflower. It is best roasted, grilled, or boiled to bring out its sweetness and nuttiness.
Visual Appeal
Purple cauliflower is more visually appealing than white cauliflower. Its vibrant color adds a pop of color to any dish, making it an excellent choice for salads, appetizers, and side dishes. White cauliflower, on the other hand, has a more traditional look and is less eye-catching.
Nutritional Comparison of Purple and White Cauliflower
While both purple and white cauliflower are nutrient-dense, there are slight differences in their nutrient profiles.
Vitamins and Minerals
Purple cauliflower contains higher levels of vitamins C and K, as well as folate and potassium, than white cauliflower. It also contains more iron, which is essential for healthy blood circulation. White cauliflower, on the other hand, has slightly more vitamin B6 and calcium than purple cauliflower.
Fiber and Carbohydrates
Both purple and white cauliflower is low in carbohydrates and high in fiber, making them an excellent choice for people following a low-carb or high-fiber diet. Purple cauliflower has slightly more fiber than white cauliflower.
Protein and Fats
Both purple and white cauliflower is low in protein and fat. However, they do contain small amounts of essential fatty acids and amino acids.
Calories and Glycemic Index
Purple and white cauliflower are both low in calories and have a low glycemic index, making them suitable food for people watching their weight or managing their blood sugar levels.
Health Benefits of Purple and White Cauliflower
Both purple and white cauliflower offer numerous health benefits.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Purple cauliflower, in particular, is rich in anthocyanins, which have powerful anti-inflammatory properties. These antioxidants can help reduce inflammation in the body and alleviate symptoms of inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, asthma, and allergies.
Antioxidant Content
Both purple and white cauliflower is rich in antioxidants that help protect the body against oxidative stress and chronic diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. These antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, can help neutralize harmful free radicals in the body.
Cancer-fighting Potential
Purple cauliflower contains higher levels of anthocyanins than white cauliflower, making it a potent cancer-fighting food. Studies have shown that anthocyanins can help prevent the growth and spread of cancer cells and induce cancer cell death in vitro and in vivo.
Digestive Health Benefits
Both purple and white cauliflower is high in fiber, which is essential for maintaining healthy digestion and preventing constipation. They also contain prebiotics, which is beneficial for promoting the growth of good gut bacteria and supporting overall gut health.
Cooking and Serving Suggestions for Purple and White Cauliflower
Purple and white cauliflower can be cooked and served in various ways.
Roasting and Grilling
Roasting and grilling are excellent ways to cook cauliflower, as they bring out its natural sweetness and nuttiness. Simply toss the cauliflower florets with olive oil, salt, and pepper, and roast or grill them until they are tender and golden brown.
Steaming and Sautéing
Steaming and sautéing are gentle cooking techniques that preserve the texture and flavor of cauliflower. To steam or sauté cauliflower, simply heat a small amount of oil or butter in a pan, add the cauliflower, and cook until it is tender and slightly browned.
Mashing and Pureeing
Cauliflower can also be mashed or pureed to make a delicious and healthy side dish. Simply boil the cauliflower until it is soft, then mash or puree it with butter, milk, and seasonings.
Serving Suggestions and Recipe Ideas
Purple and white cauliflower can be used in a variety of dishes, such as salads, soups, stews, stir-fries, and casseroles. Some recipe ideas include purple cauliflower soup, white cauliflower gratin, roasted cauliflower salad, and cauliflower fried rice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both purple and white cauliflower are excellent choices for a healthy and balanced diet. They are packed with essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants that offer numerous health benefits. While they differ slightly in their nutrient content, cooking techniques, and visual appeal, both varieties can be cooked and served in various ways and used in a variety of dishes.
Whether you prefer the milder flavor and traditional look of white cauliflower or the sweeter and more vibrant purple cauliflower, both are excellent choices for promoting overall health and well-being. Including more of these cruciferous vegetables in your diet can provide you with a range of health benefits, from reducing inflammation and preventing chronic diseases to promoting digestive health and supporting weight management.
While purple cauliflower is gaining popularity for its unique appearance and potential health benefits, both purple and white cauliflower should be included in a healthy diet. It’s important to remember that the color of the vegetable does not necessarily indicate its nutrient content, and both varieties offer numerous health benefits.
When selecting cauliflower, choose firm, compact heads with no signs of discoloration or soft spots. To store cauliflower, wrap it in a plastic bag and store it in the refrigerator for up to one week.
Incorporating cauliflower into your diet can be easy and delicious. Try adding cauliflower to your favorite stir-fry or curry, roasting it as a side dish, or pureeing it into a creamy soup. With its versatility and nutritional benefits, cauliflower is a great addition to any meal.
In summary, purple cauliflower and white cauliflower are both nutritious and delicious vegetables that offer a range of health benefits. While they differ in appearance, they are both packed with essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. Including more cauliflower in your diet can help support overall health and well-being. So, the next time you’re at the grocery store, grab some cauliflower and get creative in the kitchen!